In this article, You will read Yamuna River System – for UPSC IAS Exam.
Yamuna River System
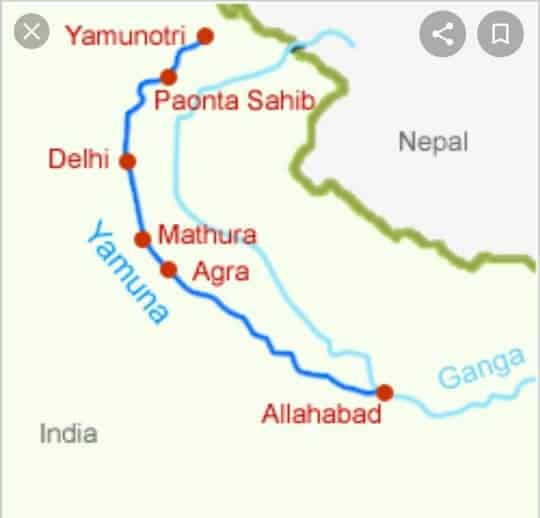
- It originates from the Yamunotri Glacier on the southwestern slopes or Banderpoonch peak in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas.
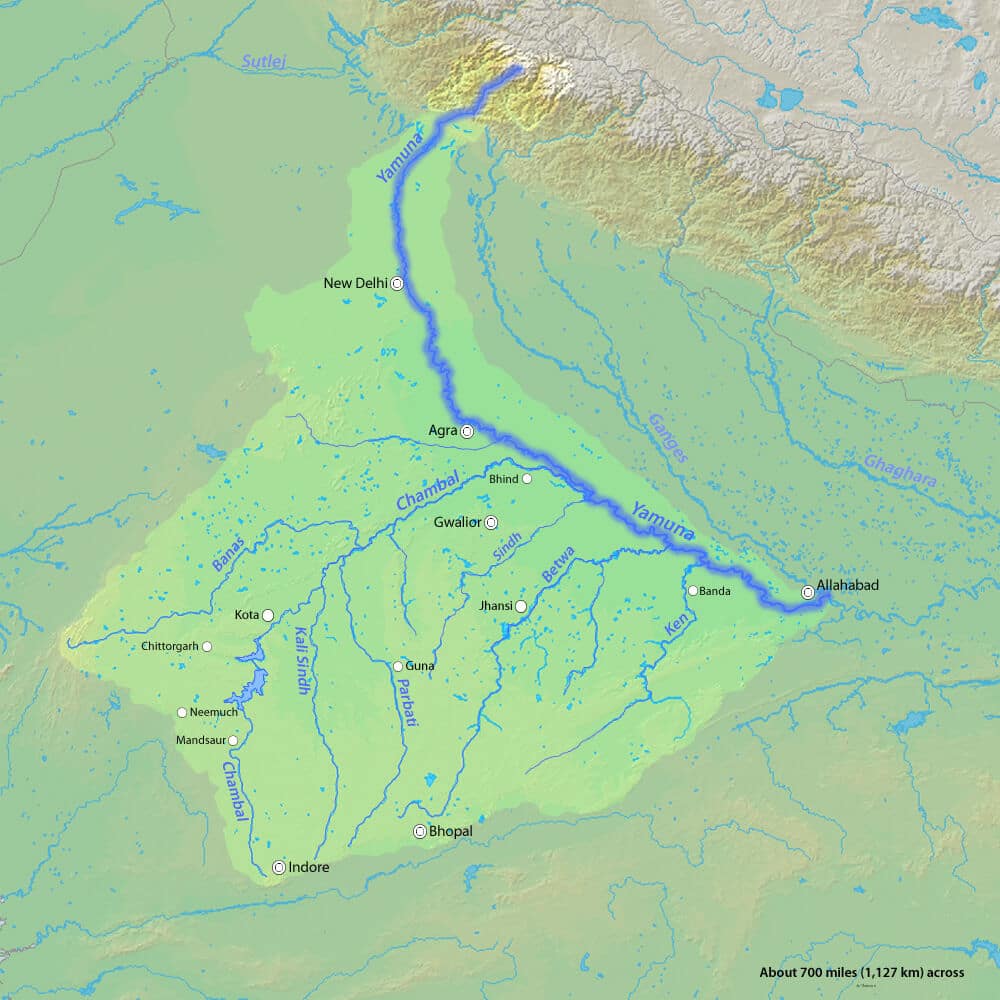
- Flows along states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana enters Delhi and merges with the Ganga near Triveni Sangam, Allahabad(Prayagraj).
- The largest tributary of the Ganga in the northern plains.
- Its main affluent in the upper reaches is the Tons which also rises from the Bandarpunch glacier.
- It joins the Yamuna below Kalsi before the latter leaves the hills.
- At this site, the water carried by the Tons is twice the water carried by the Yamuna.
- The total length of the Yamuna from its origin till Allahabad is 1,376 km.
- It creates the highly fertile alluvial, Yamuna-Ganges Doab region between itself and the Ganges in the Indo-Gangetic plain.
- The cities of Bhagpat, Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Hamirpur, and Allahabad lie on its banks.
Major Tributaries of Yamuna River
- Tons
- Giri
- Hindon
- Chambal
- Banas
- Kali Sindh
- Parbati
- Sind
- Betwa
- Dashan
- Ken
Tons River
- The Tons is the longest tributary of the Yamuna River and its flows through Garhwal, the western part of the Himalayan state of Uttaranchal.
- The river originates at an elevation of 3900 m and joins the Yamuna below Kalsi near Dehradun, Uttarakhand.
- It is one of the most major perennial Indian Himalayan rivers. It is the biggest tributaries of the Yamuna.
Giri River
- The river Giri is an important tributary of the Yamuna River. It is the main source of water in the South-Eastern Himachal Pradesh.
- The Giri is famous in the Jubbal, Rohru hills that rise from Kupar peak just above Jubbal town after flowing across the heart of Shimla hills and then flows down in the southeastern direction dividing the Sirmaur district into equal parts that are known as Cis-Giri and Trans-Giri region and join Yamuna upstream of Paonta below Mokkampur.
Hindon River
- Hindon River is an important tributary of the Yamuna River. In fact, this river is sand-witch between two major rivers: Ganga on the left and Yamuna on the right.
- Hindon originates from upper Shiwalik (Lower Himalayas). It is a purely rain-fed river with a catchment area of about 7,083 sq. km.
- This river has a total run of about 400 km.
- The width of the Hindon River ranges from 20 m to 160 m.
Chambal River
- Chambal River is also known as Charmanwati orCharmawati
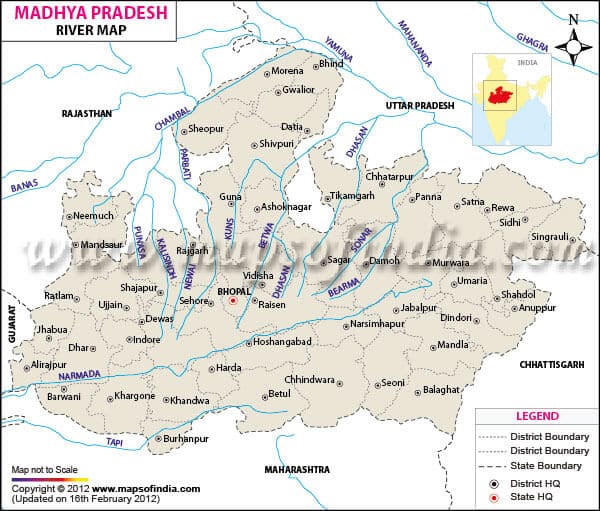
- The 960km long Chambal river originates from Janapao Hilis of the Vindhya range.
- 15km West-South-West of Mhow in Indore district in Madhya Pradesh.
- Utilized for hydropower generation at Gandhi Sagar dam, Rana Pratap Sagar dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam and the Kota Barrrage.
- The river flows much below its banks due to severe erosion because of poor rainfall and numerous deep ravines have been formed in the Chambal Valley, giving rise to badland topography. {Arid Landforms}
Dams on the Chambal
- The Gandhi Sagar dam is the first of the four dams built on the Chambal River, located on the Rajasthan-Madhya Pradesh border.
- The Rana Pratap Sagar dam is a dam located 52 km downstream of Gandhi Sagar dam on across the Chambal River in Chittorgarh district in Rajasthan.
- The Jawahar Sagar Dam is the third dam in the series of Chambal Valley Projects, located 29 km upstream of Kota city and 26 km downstream of Rana Pratap Sagar dam.
- The Kota Barrage is the fourth in the series of Chambal Valley Projects, located about 0.8 km upstream of Kota City in Rajasthan.
- Water released after power generation at Gandhi Sagar dam, Rana Pratap Sagar dam and Jawahar Sagar Dams, is diverted by Kota Barrage for irrigation in Rajasthan and in Madhya Pradesh through canals.
Keoladeo National Park is supplied with water from Chambal river irrigation project.
Banas River
- Also known as ‘Van Ki Asha'(Hope of forest),
- Originates in the Aravalli Range in Rajsamand District of Rajasthan.
- The cities of Nathdwara, Jawanpur, and Tonk lie on the river.
- Its entire, course is in Rajasthan only.
Kali Sindh
- Flows in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, that joins the Chambal River near Sawai Madhopur In Rajasthan
- Kali Sindh originates in Madhya Pradesh.
Parbati
- Originates in the northern slopes of the Vindhya Range in Madhya Pradesh, flows through Kota District and Jhalawar District of Rajasthan.
- Runs for about 436km and has a catchment area of nearly 3,070 sq miles.
- Joins the right bank of the Chambal
- The city of Guna (MP) lies on it.
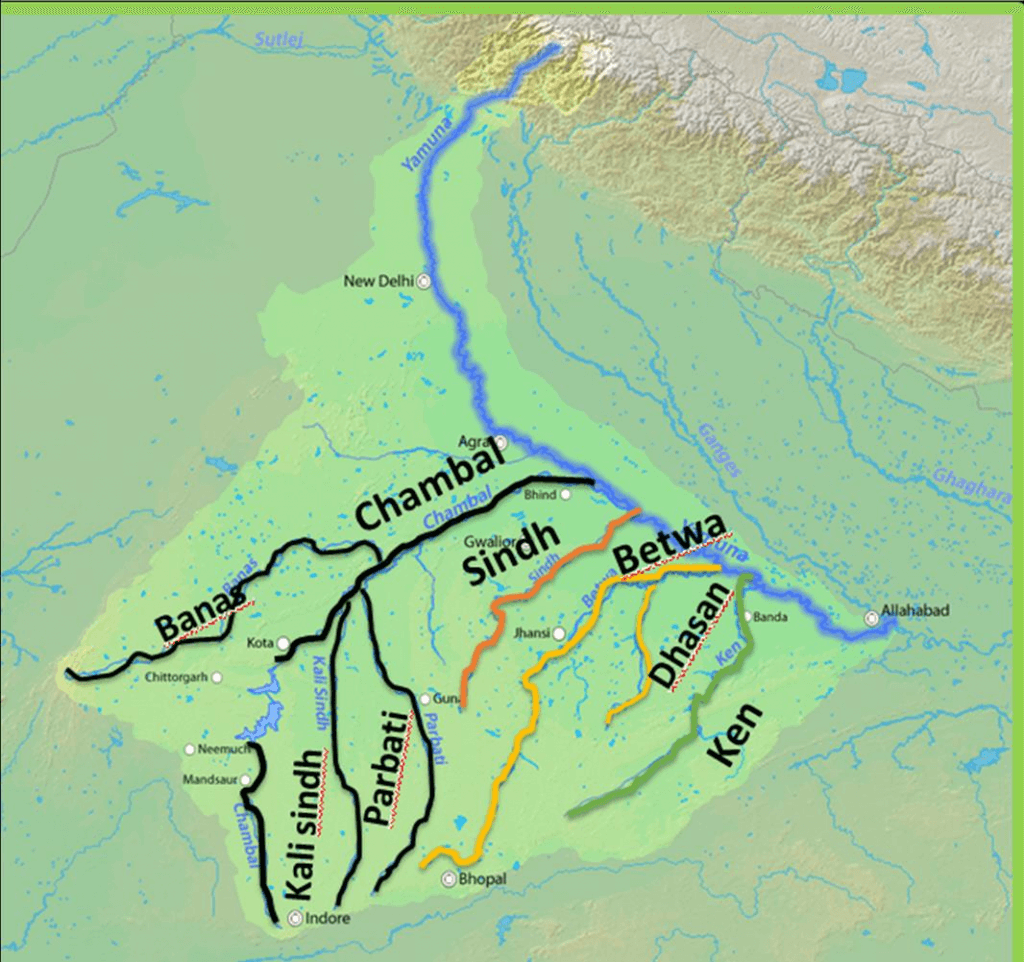
Sindh
- The Sindh originates on the Malwa Plateau in Vidisha district,
- Flows north-northeast through the districts of Guna, Ashoknagar, Shivpuri, Datia, Gwalior, and Bhind in MadhyaPradesh
- Join the Yamuna River in Etawah District, Uttar Pradesh
- Flows through Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
Betwa
- Also called as Vetravati
- Rises in the Vindhya Range north of Hoshangabad in Madhya Pradesh.
- The confluence of the Betwa and the Yamuna Rivers takes place in the Hamirpur town in Uttar Pradesh.
- Dhasan is the main tributary.
- Rajghat Dam located on the river.
Dhasan River
- It is a right-bank tributary of the Betwa River.
- Originates in Raisen District in Madhya Pradesh.
- Flows through Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
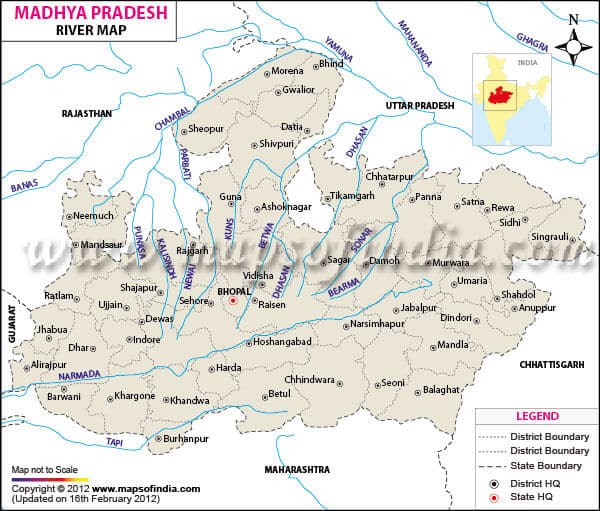
Ken River
- The Ken River originates from the slopes of Kaimur Range in Jabalpur district in Madhya Pradesh
- Merge with the Yamuna near Fatehpur in UP.
- The Ken valley separates the Rewa Plateau from the Satna Plateau.
- The Ken River passes through Penna National Park.
Important cities through which Yamuna passes
| State | Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi |
| Cities | Delhi, Noida, Mathura, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Kalpi, Hamirpur, and Prayagraj lie on its banks. |