- The Plateaus are built over millions of years as pieces of Earth’s crust smash into each other, melt, and gurgle back toward the surface.
- The term Plateau can be defined as the upland which has at least one side of a very steep slope standing well above the neighboring surface and whose upper part is extensively flat.
- The most significant deciding factor of the Plateau is the flatness of its top rather than the height.
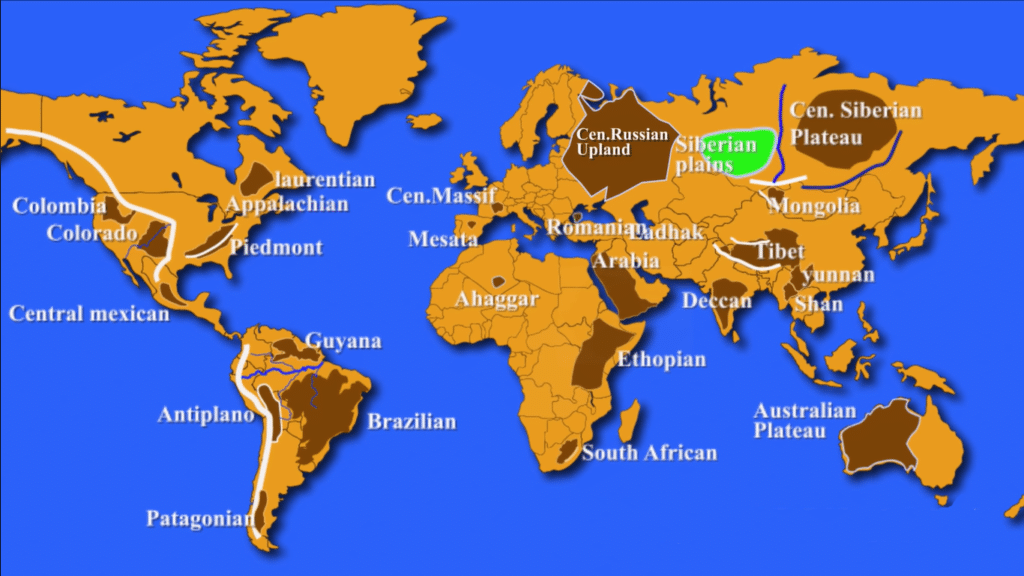
List of Major Plateaus of the World
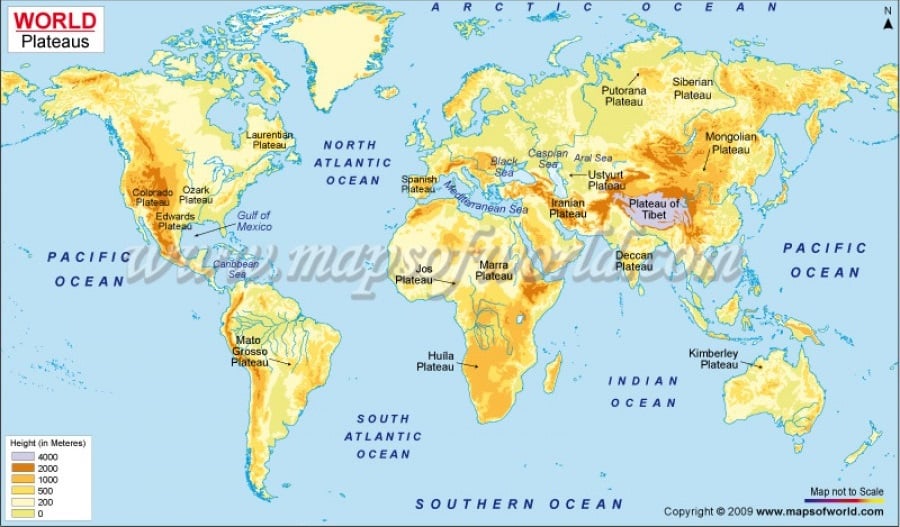
Colorado Plateau
- The Colorado Plateau includes Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico.
- It is divided by the Colorado River and the Grand Canyon.
- It is the largest plateau in America, and it covers an area of 337,000km2and its highest elevation is about 2,450m above sea level.
- This plateau is an example of intermontane plateau. Mesas and buttes are found here at many places.
- The plateau is known for the groundwater which is under positive pressure and causes the emergence of springs called Artesian wells.
Columbia Plateau
- The Columbia Plateauis located in parts of Washington, Oregon, and the Idaho states of the U.S.
- It is surrounded by the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains and it is divided by the Columbia River.
- This plateau has been formed as the result of volcanic eruptions with a consequent coating of basalt lava (Flood Basalt Plateau).
Appalachian Plateau
- The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains.
- The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States.
- The Appalachian Plateau is the northwestern part of the Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to Alabama.
Piedmont Plateau
- The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It is situated between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south.
- The Piedmont Province is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division which consists of the Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands, the Piedmont Upland and the Piedmont Lowlands sections.
Laurentian Plateau
- The Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that forms the ancient geologic core of the North American continent.
- Fine quality of iron-ore is found here.
Central Mexican Plateau
- The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano, is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico.
- It extends from the United States border in the north to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt in the south, and is bounded by the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental to the west and east, respectively.
Altiplano Plateau
- The Altiplano, Collao or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the area where the Andes are the widest.
- It is an intermontane plateau which is located between two ranges of Andes Mountain.
- It is a major area of Tin reserves.
- Capital of Bolivia La Paz and Sucre are situated on this plateau.
Guyana Highland
- The Guiana Highlands are part of the Guyana Shield, which lies in northeast South America and represent one of the oldest land surfaces in the world.
- The Guiana Shield is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate.
- It is a 1.7 billion-year-old Precambrian geological formation in northeast South America that forms a portion of the northern coast.
Brazilian Highland
- The Brazilian Highlands or Brazilian Plateau are an extensive geographical region, covering most of the eastern, southern and central portions of Brazil, in all approximately half of the country’s land area.
- The Brazilian Highland is divided into three plateaus.
- Atlantic Plateau, extending all along the eastern coast of Brazil, and including several mountain ranges. It was once almost completely covered by the Atlantic Rainforest, one of the richest areas of biodiversity in the world, of which only 7.3% remains.
- Southern Plateau, advancing inland in the southern and southern-central portions of the country. Sedimentary rocks covered partially by basaltic lava spills that form the fertile ground known as “purple land”. Large portions of this region were also covered by the Atlantic Rainforest, while araucaria highland forest and cerrado grasslands took up much of the rest.
- Central Plateau, occupying the central portions of Brazil, with sedimentary and crystalline formations. Approximately 85% was once covered by cerrado vegetation, of which only a small portion remains intact.
Patagonian Highland
- Patagonia refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile.
- It is a Piedmont plateau (Arid Landforms) lying in southern part of Argentina.
- It is a rain shadow desert plateau.
- It is an important region for sheep rearing.
Central Massif
- The Massif Central is a highland region in the middle of southern France, consisting of mountains and plateaus.
- It covers about 15% of mainland France.
- It is famous for Grapes cultivation.
Mesata
- The Meseta Central is one of the basic geographical units of the Iberian Peninsula. It consists of a plateau covering a large part of the latter’s interior.
Transylvanian Plateau
- The Transylvanian Plateau is a plateau in central Romania.
- The plateau lies within and takes its name from the historical region of Transylvania, and is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern, Southern and Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains.
- The area includes the Transylvanian Plain.
The Hardangervidda Plateau
- It is one of the largest plateaus in Europe located at a distance of about 200 km to the west of Oslo in the Hardanger region of western Norway.
- Northwest of the plateau is bordered by one of the largest glaciers of Norway.
Central Russian Upland
- The Central Russian Upland is an upland area of the East European Plain and is an undulating plateau with an average elevation of 230–250 m.
- Its highest peak is measured at 293 m.
- The southeastern portion of the upland known as the Kalach Upland.
Tibetan Plateau
- This is the highest, largest, and most famous plateau in the world; It is located in South-Central Asia and Stretches through the countries of Tibet, China, and India.
- It is 1,000 km. north to south and 2,000 km. east to west and covers an area of 2,500,000 km2 with a flat valley floor which at about 16,000 feet above sea level.
- Formed due to collision of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- The plateau is sufficiently high enough to reverse the Hadley cell convection cycles and to drive the monsoons of India towards the south.
- It is surrounded by mountains to the south by the Himalayan Range, to the northeast by the Kunlun Range, and to the west by the Karakoram Range.
Mongolian Plateau
- The Mongolian Plateau is the part of the Central Asian Plateau and having an area of approximately 3,200,000 square kilometres.
- It is bounded by the Greater Hinggan Mountains in the east, the Yin Mountains to the south, the Altai Mountains to the west, and the Sayan and Khentii mountains to the north.
- The plateau includes the Gobi Desert as well as dry steppe regions.
- It has an elevation of roughly 1,000 to 1,500 meters, with the lowest point in Hulunbuir and the highest point in Altai.
Central Siberian Plateau
- The plateau occupies a great part of central Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers.
- It is located in the Siberian Platform and extends over an area of 3,500,000 km2, between the Yenisei in the west and the Central Yakutian Lowland in the east.
- To the south it is bound by the Altai Mountains, Salair Ridge, Kuznetsk Alatau, the Eastern and Western Sayan Mountains and other mountains of Tuva, as well as the North Baikal Highlands and Baikal Mountains.
- To the north of the plateau lie the North Siberian Lowland and to the east the plateau gives way to the Central Yakutian Lowland and the Lena Plateau.
- The surface of the Central Siberian Plateau is characterized by the alternation of wide plateaus and ridges, some of the latter sharply jagged. The Central Siberian Plateau covers one-third of Siberia.
Deccan Plateau
- Deccan Plateau is a large plateau which forms most of the southern part of India.
- It is bordered by two mountain ranges, the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats.
- The plateau includes the Deccan Traps which is the largest volcanic feature on Earth.
- Made of multiple basalt layers or lava flows, the Deccan Traps covers 500,000 square kilometers in area.
- The Deccan Traps are known for containing some unique fossils.
- The Deccan is rich in minerals. Primary mineral ores found in this region are mica and iron ore in the Chotanagpur region, and diamonds, gold and other metals in the Golconda region.
Yunnan Plateau
- The Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau or Yungui Plateau is a highland region located in southwest China.
- The region is primarily spread over the provinces of Yunnan and Guizhou.
Shan Plateau
- Shan Plateau, crystalline massif forming the eastern part of Myanmar (Burma) and forming part of the Indo-Malayan mountain system.
- The plateau is crossed by the deep trench of the Salween River in the east and is bordered by the upper course of the Irrawaddy River to the west.
- The average elevation of the plateau is between 2,500 and 4,000 feet (750 and 1,200 m).
- It is seamed and ribbed by mountain ranges that split up and run into each other.
Arabian Plateau
- The Arabian Peninsula is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate.
- Arabian Plateau is an Oligocene sub-horizontal regional planation surface, extending throughout the western half of the Arabian Peninsula.
- Its present elevation of about 1 km required a prominent uplift since the Late Eocene.
Anatolian Plateau
- Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent.
- It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey.
- It is an intermontane plateau lying between Pontiac and Taurus Mountain ranges.
- Tigris–Euphrates Rivers flow through this plateau.
- Precious wool producing Angora goats are found here.
Ethiopian Plateau
- The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in northeast Africa.
- It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below 1,500 m, while the summits reach heights of up to 4,550 m.
East African Plateau
- East African Plateau is a large plateau in the eastern part of central Africa in Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania.
- Its elevation is mostly between 1000 and 1500 meters.
- It is subdivided into a number of zones running north and south and consisting in turn of mountain ranges, tablelands, and rift valleys.
Table Mountain
- Table Mountain is a prominent landform located in Cape Town in South Africa.
- It is located at the northern end of the Sandstone Mountain Range.
- To its south is the part of the range known as the Back Table. It is a level plateau measuring 3m from side to side.
Ahaggar Plateau
- Ahaggar, also spelled Hoggar, large plateau in the north centre of the Sahara, on the Tropic of Cancer, North Africa.
- Its height is above 3,000 feet (900 m), culminating in Mount Tahat (9,573 feet [2,918 m]) in southeastern Algeria.
Katanga Plateau
- The Katanga, or Shaba, Plateau is a farming and ranching region in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- It is famous for copper production.
- Other minerals like Cobalt, Uranium, Zinc, Silver, Gold and Tin are also mined here.
Western Plateau (Australian Shield)
- The Western Plateau is Australia’s largest drainage division and is composed predominantly of the remains of the ancient rock shield of Gondwana.
- It covers two thirds of the continent; 2,700,000 square kilometres of arid land, including large parts of Western Australia, South Australia, and the Northern Territory.
- For comparison, it is roughly the same size as the whole of continental Europe from Poland west to Portugal.
- Most of the territory is flat sandy or stony desert with a sparse covering of shrubs or tussock grasses.
Kimberley Plateau
- Kimberley, also called the Kimberleys, plateau region of northern Western Australia, extending from the rugged northwest Indian Ocean coast south to the Fitzroy River and east to the Ord River.
- This plateau is made of volcanic eruption.
- Many minerals like iron, gold, lead, zinc, silver and diamond are found here.
- It is a mining and cattle rearing region of northwest Australia.
The Atherton Tableland
- The Atherton Tableland is located in Queensland, Australia.
- It covers an area of 32,000km2and has an elevation of 500 to 1,280m above sea level.
The Antarctic Plateau
- This plateau is located in Central Antarctica and cuts across parts of the South Pole and the Amundsen Scott Station.
- This plateau covers an area of 1,000km2and has its highest elevation of about 3,000m above sea level.
The Potohar Plateau
- The Potohar Plateau is located in the northeastern part of Pakistan.
- The plateau is bordered by the Jehlum River to the east, by the Indus River to the west, by the Margalla Hills and the Kala Chitta Range to the north, and by the Salt Range to the south.
- The plateau encompasses four districts which include Jehlum, Chakwal, Rawalpindi, and Attock.
Mascarene Plateau
- Plateaus also form in the ocean, such as the Mascarene Plateau in the Indian Ocean.
- It extends between the Seychelles and Mauritius Islands.
Loess Plateau
- It is in China. The soil here is made of fine particles brought by the wind. This fine loamy soil is extremely productive. Crops grown in this soil along the Yellow River give great yields.