In this article, You will read Krishna River System – for UPSC IAS.
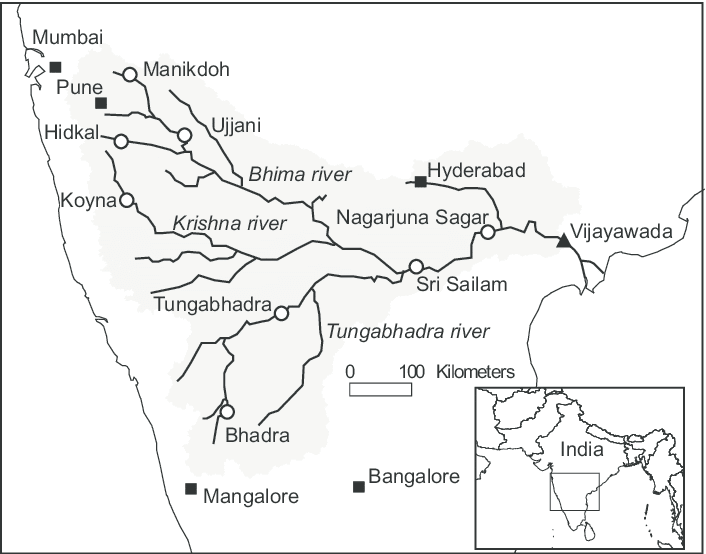
Krishna River System
- The Krishna is the second-largest east-flowing river of the Peninsula.
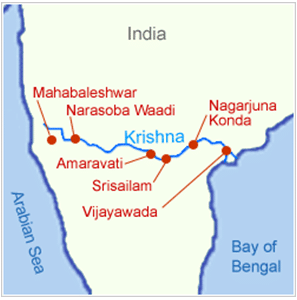
- Krishna river rises at Mahabaleshwar at an altitude of I336 m near the Jor village in the extreme north of district Satara, Maharashtra in the west, and meets the Bay of Bengal in Andhra Pradesh, on the east coast.
- Ecologically, this is one of the disastrous rivers in the world, in that it causes heavy soil erosion during the monsoon season.
- It is bounded by the Balaghat range on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and the east, and by the Western Ghats on the west.
- The total length of the river from origin to its outfall into the Bay of Bengal is 1,400 km.
- The major part of the basin is covered with agricultural land accounting to 75.86% of the total area.
- The Krishna forms a large delta with a shoreline of about 120 km.
- Almatti Dam, Srisailam Dam, Nagarjuna Sagar Dam, and Prakasham Barrage are some of the major dams constructed on the river.
- Because it is fed by seasonal monsoon rains, the river’s flow undergoes great fluctuation during the year, limiting its usefulness for irrigation.
- Satara, Karad, Sangli, Bagalkot. Srisailant, Amaravati, and Vijayawada are some of the important urban and tourist centers on the bank of the river.
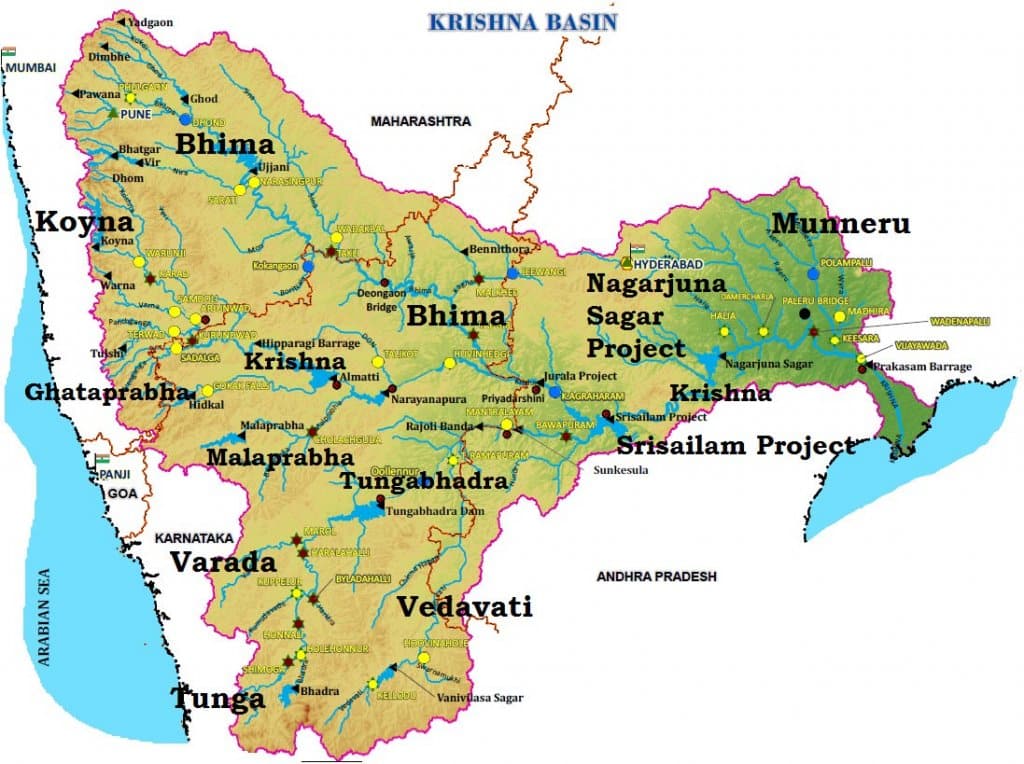
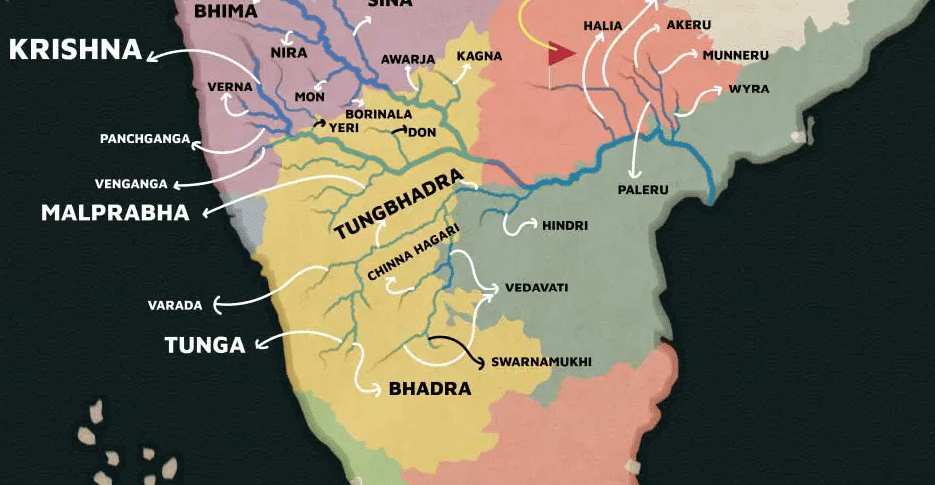
Tributaries of Krishna River
- Right bank: Venna, Koyna, Panchganga, Dudhganga, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha and Tungabhadra are the major right-bank tributaries
- Left Bank: Bhima, Dindi, Peddavagu, Halia, Musi, Paleru, and Munneru are the major left-bank tributaries
- The Koyna is a small tributary but is known for Koyna Dam. This dam was perhaps the main cause of the devastating earthquake (6.4 on Richter scale) in 1967 that killed 150 people.
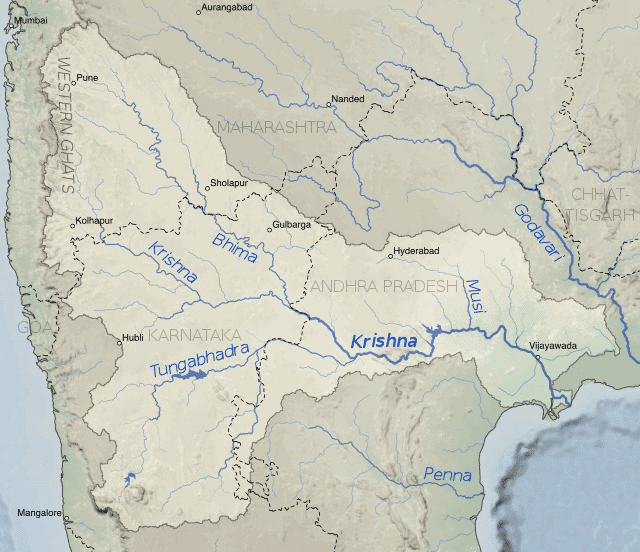
- The Bhima originates from the Matheron Hills and joins the Krishna near Raichur after for a distance of 861 km.
- The Tungabhadra is formed by the unification of the Tunga and the Bhadra originating from Gangamula in the Central Sahyadri. Its total length is 531 km.
- At Wazirabad, it receives its last important tributary, the Musi, on whose banks the city of Hyderabad is located.
BHIMA
- It originates in Bhimashankar hills near Karjat on the western side of Western Ghats (known as Sahyadri), in Maharashtra.
- Bhima flows southeast for 725 km through Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh states.
- Bhimashankar (one of the twelve esteemed Jyotirlinga shrines); Siddhatek, Siddhivinayak Temple of Ashtavinayak Ganesh: Pandharpur Vithoba Temple: Sri Dattatreya Temple: and Sri Kshetra Rasangi Balibheemasena Temple are some of the important temples located on the banks of the river.
MUSI
- Also known as the Muchukunda river in the olden days, the Musi River, a tributary of Krishna River, originates in Anantagiri Hills near Vikarabad, Rangareddi district, 90km west of Hyderabad
- In 1920, the Osmansagar reservoir was constructed across the river at Gandipet village
- Another important dam is Himayat Sagar, Hussain Sagar Lake was built on a tributary of the River Musi, Together they act as a source of water for Hyderabad.
- Musi River is also the bowl for water festivals such as boating races, decorated boating contest, and river swimming tournament.
KOYNA
- It rises in Mahabaleshwar in Satara district of Maharashtra and is a tributary of the Krishna River
- Unlike most of the other rivers in Maharashtra which flow East-West direction, the Koyna River flows in a North-South direction
- The Koyna River is famous for the Koyna Dam which is the largest hydroelectric project in Maharashtra
- The reservoir – Shivasagar Lake, is a huge lake of 50 km in length
- The dam is situated in Koyna Nagar in the Western Ghats
- The river meets the Krishna River at Karad
- The river is just about 100 in width and is slow-flowing.
PANCHGANGA
- The Panchganga River flows through the borders of Kolhapur.
- The Panchganga is formed by four streams: the Kasari, the Kumbhi, the Tulsi, and the Bhogawati.
- The Prayag Sangam confluence marks the beginning of the Panchganga River proper which after receiving the waters of the four tributaries continues in a larger pattern with the flow of waters received from the rivers, From North of Kolhapur, it has a wide alluvial plain.
- After developing this plain the river resumes its course eastwards. It falls into the Krishna at Kurundvad.
DUDHGANGA
- It is a right-bank tributary of the-river Krishna
- It is an important river of the Kolhapur district
- The Kallammawadi Dam has been built on the Dudhganga River in collaboration with the Karnataka State.
GHATAPRABHA
- Ghataprahha River originates in the Western Ghats at an altitude of 884 m and flows eastward for a distance of 283 km across Karnataka and Maharashtra states before its confluence with the Krishna River at Almatti.
- The Gokak waterfall on the river in Belgaum District is a noted tourist attraction
- The Ghataprabha Project is a hydroelectric and irrigational dam across the river.
MALAPRABHA
- Malaprabha originates in Kanakumbi of Belgaum District in Karnataka, at an altitude of 792 m in the Sahyadris
- It flows for a distance of 304 km and joins the Krishna River at an altitude of 488 m at Kudalasangama in Bagalkot district in Karnataka
- The Navilatirtha Dam is constructed near Munavalli in Belgaum District. Its reservoir is called Renukasagara
- Famous temples of Aihole Pattadakal and Badami are located on the Banks of this river. These are listed as World Heritage sites by UNESCO.
TUNGABHADRA
- The ancient name of the river was Pampa
- The Tungabhadra river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, the Tunga River and the Bhadra River, which flow down the eastern slope of the Western Ghats in the state of Karnataka
- From there, Thungabhadra meanders through the plains to a distance of 531 km and mingles with the Krishna at Gondimalla, near the famous Alampur Jn in Mahaboobnagar District of Andhra Pradesh.
- Varada, Hagari, and Handri are the main tributaries of the Tungabhadra
- The wedge of land that lies north of the Tungabhadra River, between the Tungabhadra and the Krishna, is known as the Raichur Doab.
- Harihar, Hospet. Hampi, Mantralayam, and Kurnool are the major urban centers on the river.
Projects on Krishna River
- Important ones are the Tungabhadra, Ghataprabha, Nagarjunasagar, Malaprabha, Bhima, Bhadra and Telugu Ganga.
- The major Hydro Power stations in the basin are Koyna, Tungabhadara, Sri Sailam, Nagarjuna Sagar, Almatti, Naryanpur, Bhadra.
- Tunagabhadra is a major inter-States project in the basin. In order to operate the project and to regulate the flows among the beneficiary States of Karnataka and Andhara Pradesh.
- The Tungabhadra Project– The project aims at producing hydro-electricity, providing irrigation water and municipal water supply, and controlling floods in the region. Under this project, a dam has been constructed across the Tungabhadra river near Hospet in the state of Karnataka.
- The Srisailam Project– Under the project, a large dam has been constructed across the Krishna river in Kurnool district in the state of Andhra Pradesh. It has created a reservoir named as Srisailam Sagar or Neelam Sanjjeva Reddy Sagar.
- The Nagarjuna Sagar Dam– The construction of the dam started in 1950, being one of the earliest large infrastructure projects of India, aimed at bringing the Green Revolution. The dam has been constructed across the Krishna river straddling the borders of the Nalgonda and Guntur districts.
- The Prakasam Barrage– The Prakasam Barrage was conceptualized by Major Cotton of the East India Company. It is constructed across the Krishna river near Vijayawada in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
- The Ghatprabha Project– The project has been executed across the Ghatprabha river near Chandgad in Kolhapur district in the state of Maharashtra in the Krishna river basin.
- The Bhima Project– The project has been executed across the Bhima river in the Solapur district in the state of Maharashtra in the Krishna river basin.
Resources in Krishna Basin
- The basin has rich mineral deposits and there is good potential for industrial development.
- Iron and steel, cement, sugar cane vegetable oil extraction, and rice milling are important industrial activities at present in the basin.
- Recently oil has been struck in this basin which is bound to have an effect on the future industrial scenario of this basin.
Industry in Krishna Basin
- The major Urban Centers in the Basin are Pune, Hyderabad.
- Hyderabad is the state capital of Telangana and is now a major IT hub.
- Pune in Maharashtra has number of automobile and IT industry and is major education centre.
Drought and Floods in Krishna Basin
- Some parts of the basin, especially the Rayalaseema area of Andhra Pradesh, Bellary, Raichur, Dharwar, Chitradurga, Belgaum, and Bijapur districts of Karnataka and Pune, Sholapur, Osmanabad, and Ahmedanagar districts of Maharashtra are drought-prone.
- The delta area of the basin is subject to flooding. It has been observed that the river bed in the delta area is continuously raised due to silt deposition resulting in a reduction in the carrying capacity of the channel.
- The coastal cyclonic rainfall of high intensity and short duration makes the flood problem worse.