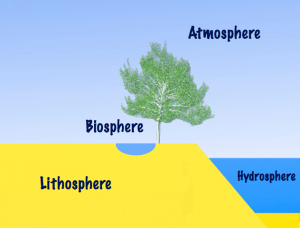
Major domains of the earth are a basic concept in Geography. The earth’s surface is a complex zone in which the three major components of the environment meet, overlap and interact. Solid (Lithosphere), gaseous (Atmosphere), liquid (Hydrosphere) and biosphere parts of the earth are not isolated, but they overlap with each other.
The Four Domains of the Earth
- Lithosphere: The solid portion of the earth
- Atmosphere: The gaseous layers that surround the earth
- Hydrosphere: Water covers a very big area of the earth’s surface and this area is called the Hydrosphere
- Biosphere: It is the narrow zone where land, water, and air together are found.
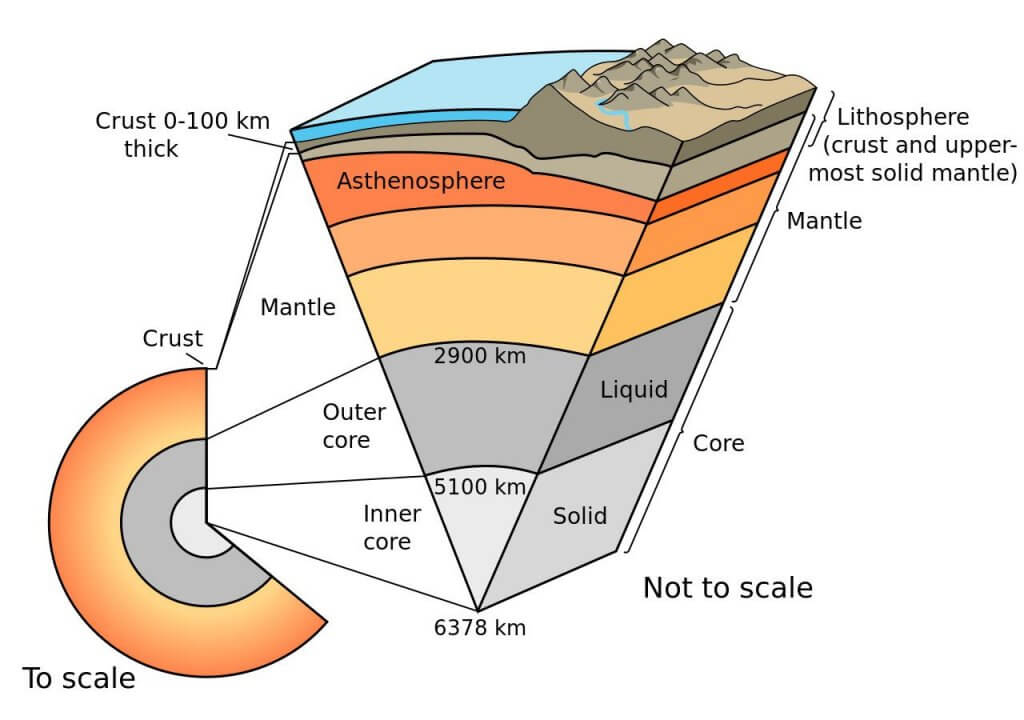
Lithosphere
- The outermost part of the Earth which consists of Upper Mantle and Crust of the Earth is known as Lithosphere.
- Tectonic plates are a subdivision of Lithosphere.
- Lithosphere has rigid mechanical properties. Pedosphere is the uppermost part of the lithosphere which reacts chemically with other 3 other major domains of earth namely; hydrosphere, biosphere and atmosphere.
- Thickness – about 100 km.
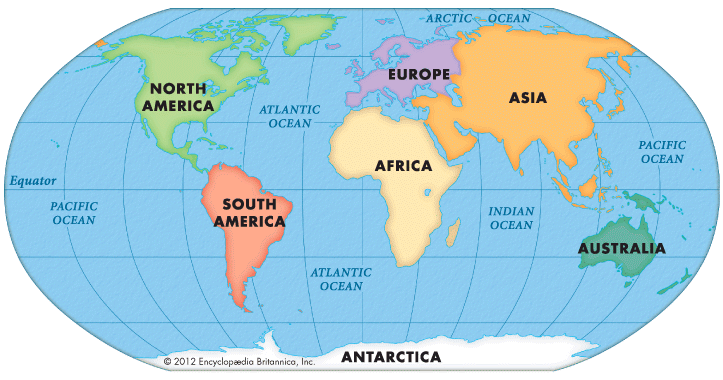
Continents
There are seven major continents and these are separated by large water bodies.
- Asia
- Asia is the largest continent covering one-third of the total land area of the earth.
- The continent lies in the Eastern Hemisphere.
- The Tropic of Cancer passes through Asia.
- The Ural Mountains on the west separates from Europe.
- Europe
- Europe is much smaller than Asia lying to the west of Asia.
- The Arctic Circle passes through it.
- Its three sides are bound by water bodies.
- Africa
- Africa is the second-largest continent after Asia.
- A large part of Africa lies in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Africa is the only continent through which the Tropic of Cancer, the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn pass.
- North America
- North America is the third largest continent in the world.
- The continent lies completely in the Northern and Western Hemisphere.
- The Isthmus of Panama a narrow strip links North America and South America.
- This continent is surrounded by three oceans and they are the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean.
- South America
- South America lies mostly in the Southern Hemisphere.
- It is surrounded by two oceans; the Pacific Ocean on the west and the Atlantic Ocean on the east and north.
- Australia
- Australia is the smallest continent that lies entirely in the Southern Hemisphere.
- It is surrounded on all sides by the oceans and seas.
- It is called an island continent.
- Antarctica
- Antarctica is a huge continent and lies completely in the Southern Hemisphere.
- The South Pole lies in the South Polar Region almost at the centre of this continent and is permanently covered with thick ice sheets.
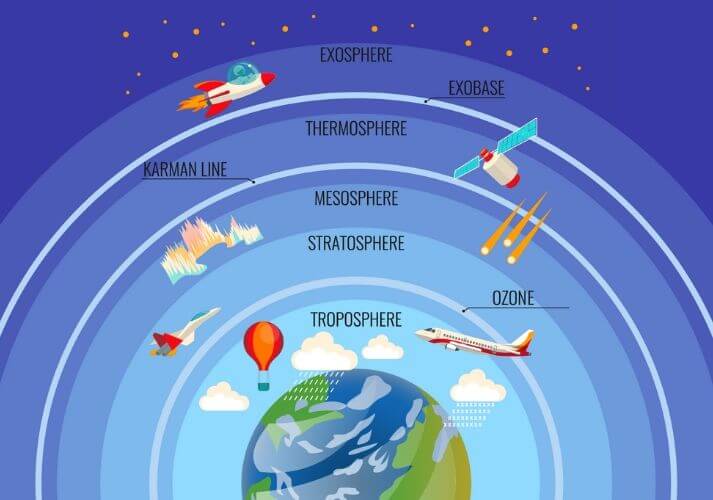
Atmosphere
- The earth is surrounded by a layer of gas called the atmosphere.
- The gaseous layers that surround the earth— where oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and other gases are found and interact
- The changes in the atmosphere produce changes in the weather and climate.
- The atmosphere extends up to a height of about 1,600 kilometres.
- The gravitational force of the earth holds the atmosphere around it
- The atmosphere is divided into five layers based on composition, temperature and other properties and they are:
- the troposphere
- the stratosphere
- the mesosphere
- the thermosphere
- the exosphere
- About 99 per cent of clean and dry air in the atmosphere is composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen. Nitrogen 78 per cent, oxygen 21 per cent and other gases like carbon dioxide, argon and others comprise 1 per cent by volume.
- The density of the atmosphere: Maximum at the sea level and decreases rapidly as we go up.
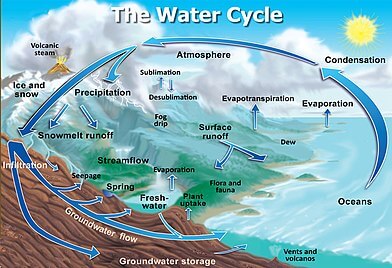
Hydrosphere
- The earth is called the blue planet.
- More than 71 per cent of the earth is covered with water and 29 per cent is with the land. Hydrosphere consists of water in all its forms.
- More than 97% of the Earth’s water is found in the oceans and is too salty for human use.
- Hydrosphere consists of water in all its forms like running water in oceans and rivers and in lakes, ice in glaciers, underground water and the water vapour in the atmosphere.
- 97% of the Earth’s water is found in the oceans and is too salty, the rest of the water is in the form of ice sheets and glaciers or under the ground and a very a small percentage is available as freshwater for human use
Oceans
- The three chief movements of ocean waters are the waves, the tides and the ocean currents.
- Oceans are the major part of the hydrosphere and they are all interconnected.
- The five major oceans in order of their size are
- the Pacific Ocean: It is almost circular in shape. Asia, Australia, North and South Americas surround it.
- the Atlantic Ocean: It is the second-largest ocean in the world. It is ‘S’ shaped. It is flanked by the North and South Americas on the western side, and Europe and Africa on the eastern side.
- the Indian Ocean: It is the only ocean named after a country, that is, India. The shape of the ocean is almost triangular. In the north, it is bound by Asia, in the west by Africa and in the east by Australia.
- the Southern Ocean: It surrounds the continent of Antarctica
- the Arctic Ocean: It is located within the Arctic Circle and surrounds the North Pole. The Barring strait a narrow stretch of shallow water connects it with the Pacific Ocean.
Biosphere – The Domain of Life
- The biosphere is the narrow zone of contact between the land, water and air.
- It is the zone where life exists that makes this planet unique.
- The organisms in the biosphere are commonly divided into:
- the plant kingdom
- the animal kingdom
- The three domains of the earth interact with each other and affect each other in some way or the other.
References: NCERT, G C Leong, Wikipedia
No comments:
Post a Comment