You all know that ocean water is never still. There are different types of movements of ocean water under the influence of different physical characteristics like temperature, salinity, density, etc. Movements of ocean water are also affected by external forces like the sun, moon, and winds.
Motion of Ocean water can be classified in two direction –
- HORIZONTAL
- VERTICAL
Horizontal movements of the ocean waters can be classified into two –
- WAVES
- CURRENTS
Vertical movements of the ocean waters can be classified into two –
- TIDES
- UPWELLING
Ocean Waves
Wave is a rhythmic movement that carries energy through matter or space.
Ocean Waves are the undulatory motion of a water surface.
- Waves are nothing but the oscillatory movements that result in the rise and fall of the water surface.
- Waves are a kind of horizontal movement of ocean water.
- They are actually the energy, not the water as such, which moves across the ocean surface.
- This energy for the waves is provided by the wind.
- In a wave, the movement of each water particle is in a circular manner.
- A wave has two major parts: the raised part is called the crest while the low-point is called the trough.
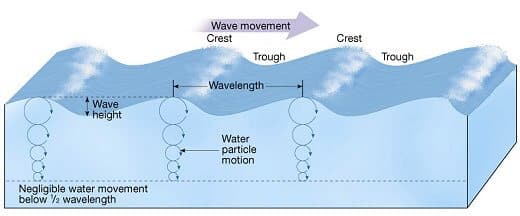
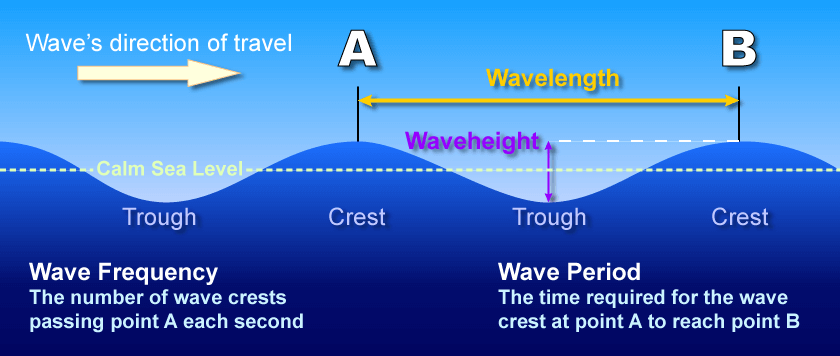
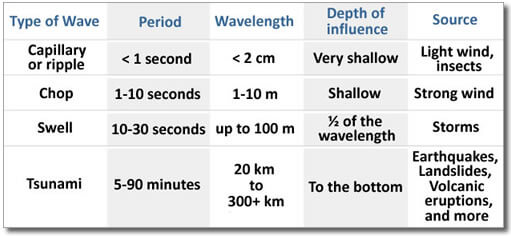
Parts of a wave
| Wave crest and trough | The highest point of a wave is called crest. The lowest point of a wave is called trough. |
| Wave height | It is the perpendicular distance from the bottom of a trough to the top of a crest of a wave. |
| Wave amplitude | It is one-half of the wave height. |
| Wave period | It is merely the time interval between two successive wave crests or troughs as they pass a fixed point. |
| Wavelength | It is the horizontal distance between two successive crests. |
| Wave speed | It is the rate at which the wave moves through the water. It is measured in knots. |
| Frequency | the number of complete waves (or oscillations) that occur over a given period of time. Usually measured in cycles per second. |
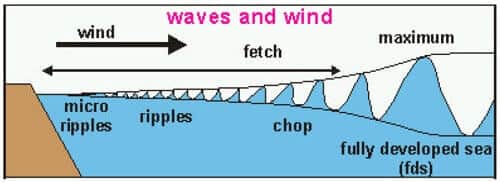
Most of the waves present on the ocean’s surface are wind-generated waves.
Friction from the wind moving over the water causes the water to move along with the wind. If the wind speed is high enough, the water begins to pile up and a wave is formed.
As wind velocity increases: Wavelength, Wave period, Height Increase.
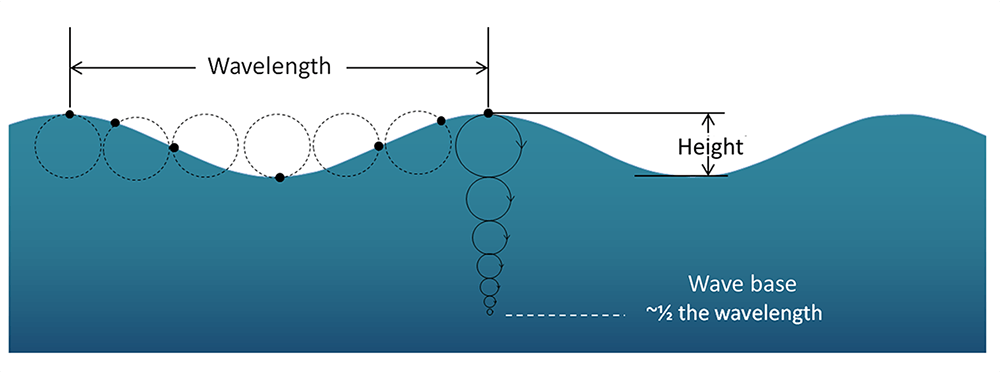
Water molecules move in an orbital motion as the wave passes.
Particles of water move around in circles. The farther below the surface, the smaller the circle.
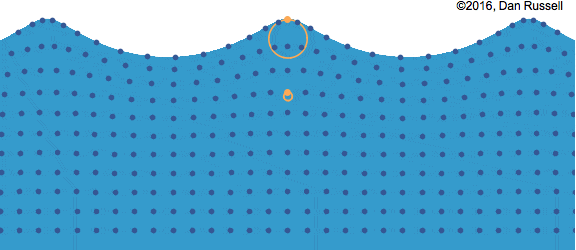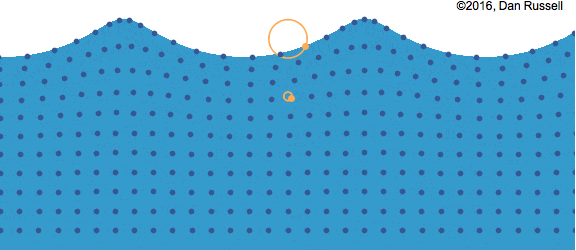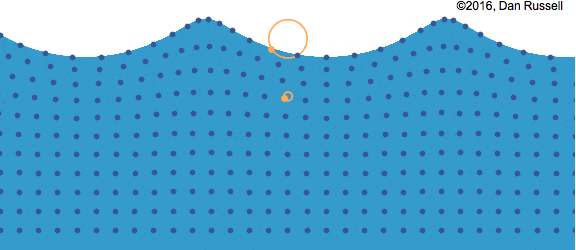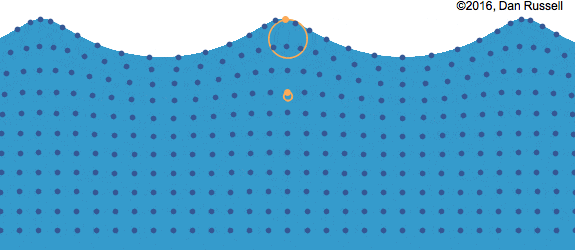
The diameter of the orbit: increases with increasing wave size.
The diameter of the orbit: decreases with depth below the water surface.
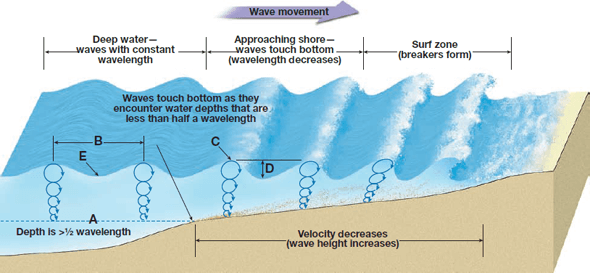
As the wave slows, its crest and trough come closer together. The top of the wave is not slowed by friction and moves faster than the bottom.

Wave types
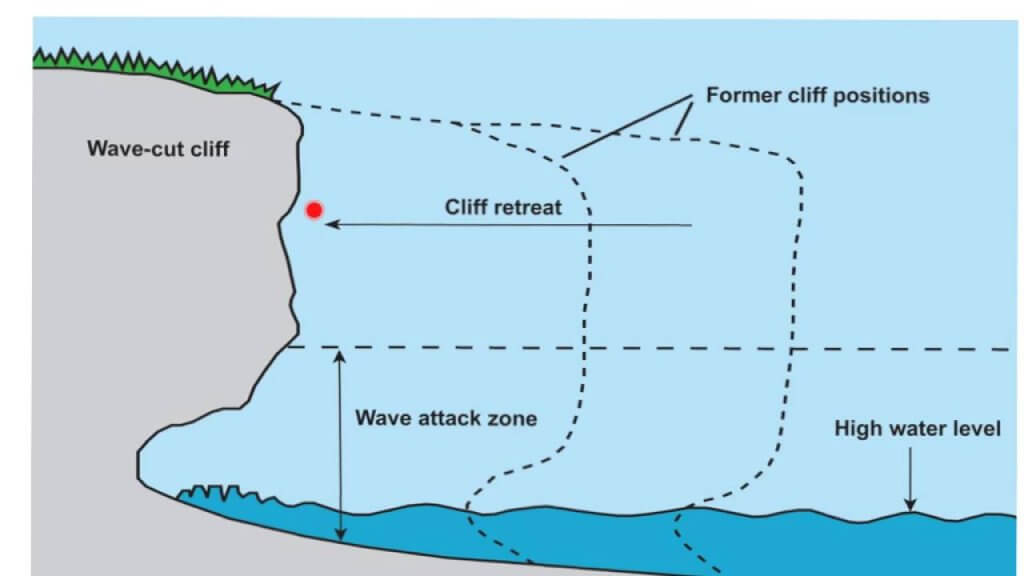
Wave Cut action
Comments
Post a Comment