In this article, You will read Western Disturbances: Effects & Benefits for India – for UPSC IAS.
Western Disturbances
- Western Disturbances develop in the mid-latitude region (north of the Tropic of Cancer), not in the tropical region, therefore they are called as mid-latitude storms or extra-tropical storms.
- Extra-Tropical Cyclones are also called as winter storms and blizzards.
- It is a term coined by an Indian Meteorologist for the weather phenomenon which is propagated from the West.
- The phrase Western Disturbance was first used in published literature in 1947. However, its precursor Winter Disturbance was coined earlier in 1931.
- Western Disturbances are low-pressure systems, embedded in western winds (westerlies) that flow from west to the east.
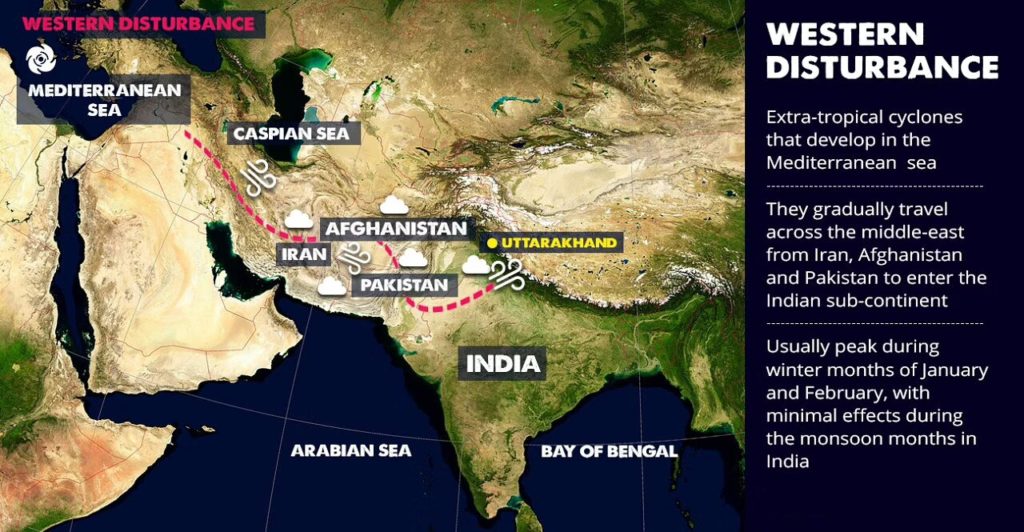
- The low pressure typically forms over the Mediterranean Sea and travels over Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, and Pakistan before entering India loaded with moisture.
- These moisture-laden western disturbances eventually come up against the Himalayas and get blocked, as a consequence, the moisture gets trapped and precipitation is shared in the form of snow and rain over Northwest India and sometimes, other parts of North India.
- An average of 4-5 western disturbances form during the winter season and the rainfall distribution and amount varies with every western disturbance.
- The word ‘Western’ refers to the direction from which they originate with regard to India.
- The word ‘disturbance’ is used because the air within the low-pressure systems tends to be unstable or disturbed.
- Sometimes, when western disturbances become more intense in the Indian Region, they can extend even up to 15 degrees north, resulting in rainfall up to north Maharashtra, Gujarat, and the entire Madhya Pradesh to the south.
Formation of western disturbances
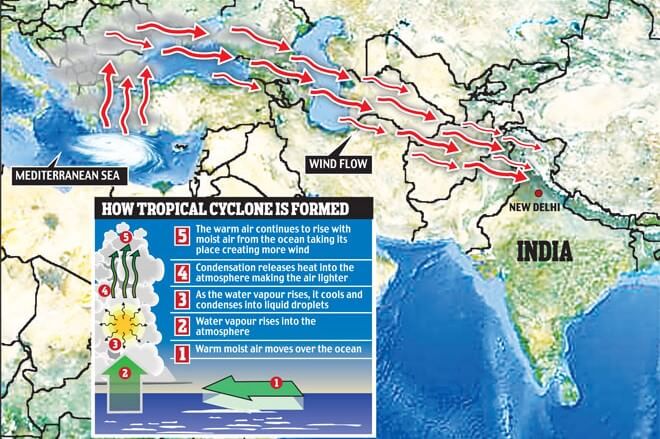
- Western Disturbance has its origin in the Mediterranean Sea as extra-tropical cyclones.
- A high-pressure is exhibited area over the areas like Ukraine and neighborhood countries causes the intrusion of cold air from Polar Regions towards an area of relatively warmer air with high moisture. This change in pressure from cold air to warm air generates favorable conditions for cyclogenesis in the upper layer of the atmosphere, which promotes the formation of an eastward-moving extratropical depression in the sea.
- Then these gradually travel across the middle-east from Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan to finally enter the Indian sub-continent.
Impact
- Western Disturbances are the cause of the most winter and pre-monsoon season rainfall across North-West India. This phenomenon is usually associated with a cloudy sky, higher night temperatures, and unusual rain. It is estimated that India gets close to 5-10% of its total annual rainfall from western disturbances.
- In winter, western winds bring moderate to heavy rain in low lying areas and heavy snow to mountainous areas of the Indian subcontinent.
- India is a rain-dependent country and while the southwest monsoon covers most of India, parts of North India don’t get much rain from it. These regions depend upon snow and rain from western disturbance during the winter season from November to March.
- Precipitation during the winter season has great importance in agriculture particularly for rabi crops including wheat, which is one of the most important Indian crops.
- They start declining after winter. During the summer months of April and May, they move across North India and at times help in the activation of monsoon in certain parts of northwest India.
- During the monsoon season, western disturbances may occasionally cause dense clouding and heavy precipitation.
- Weak western disturbances are associated with crop failure and water problems across north India.
- Strong western disturbances can help residents, farmers and governments avoid many of the problems associated with water scarcity.
Casualties
- Since western disturbances are not high-intensity weather systems, they are not usually associated with disasters but in the recent past, it is observed that this beneficial weather phenomenon is increasingly becoming disastrous during the summer and monsoon seasons.
- The 2010 cloudburst in Leh, in which 71 towns and villages were damaged and 225 people died was caused due to the western disturbances.
- In September 2014, the Kashmir region suffered disastrous floods across many of its districts killing over 200 people. This was also caused by the Western Disturbances.
- Expert opinion on western disturbances is divided regarding the 2013 floods in Uttarakhand in which over 5000 people were killed, after three days of incessant rainfall. While many believe that Uttarakhand floods may have occurred due to interactions between western disturbances and the summer monsoon, many others believe that western disturbances and monsoon occur in completely different time frames.
Importance of Western Disturbances
- The western disturbances affect weather conditions during the winter season up to Patna (Bihar) and give occasional rainfall which is highly beneficial for the standing rabi crops, (wheat, barley, mustard, gram, lentil, etc.).
Cloudburst
- A cloudburst is an intense torrential rainfall brought by a thunderstorm that lasts for a relatively short duration (few minutes to few hours).
- Cloudburst leads to flash floods and causes a lot of damage to life and property.
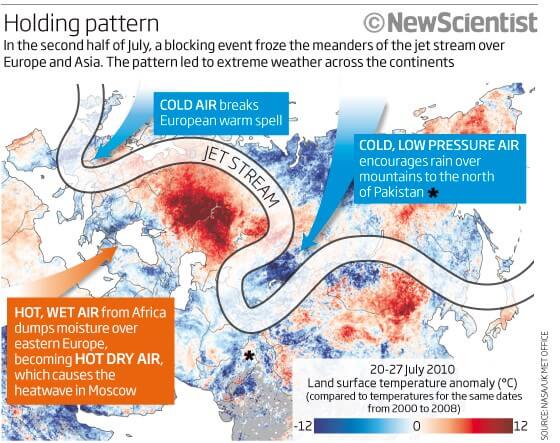
- Every intense rainfall is not a Cloudburst. Cloudburst specifically occurs when an air mass with high humidity is struck at a place due to various reasons. In 2010, the South-Western strip of Russia (Caucasus Region, Moscow, etc.) saw higher than normal temperatures (highest in the last 100 years) and there were numerous cloudbursts in Jammu and Kashmir.
- A strong upper-atmospheric high was located over European Russia towards the beginning of summer.
- It diverted the jet stream (meandering of Sub-Tropical Jet Stream) and its rain-giving train (trough) of summer storms farther north than usual, giving much of Southern European Russia drought conditions.
- In addition, southern desert heat from central Asia, the Arabian Peninsula, and North Africa began to flow northward, which strengthened this ridge of STJ and tightened its hold over the region.

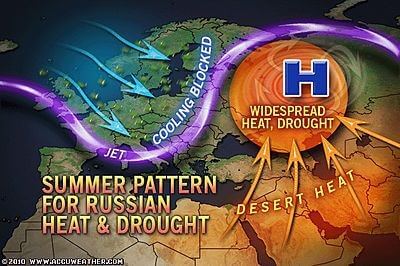
- The stalled system prevented weather systems from being drawn across Russia and the obstacle acted as a barrier trapping hot air to the south and cold air to the north.
- The consequence of this static mass of hot air was the heatwave that devastated Russia.
- With the jet stream stalled the Sub-Tropical Jet was unable to transit across the Himalayas as it would do ordinarily, the monsoon cell to the south, fed by warmer waters in the Indian Ocean, had nowhere to go and as a consequence, it deposited vast amounts of rain over Pakistan, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir and this led to extensive flooding.