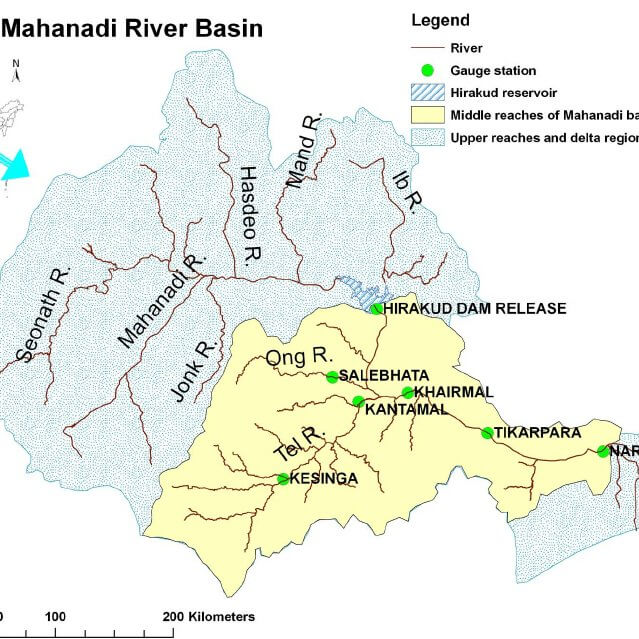
The Mahanadi River system is the third largest of peninsular India and the largest river of Odisha state. The word Mahanadi is a compound of the two Sanskrit words maha which means”great” and nadi which means”river”.
Mahanadi River system
- The Mahanadi basin extends over states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and comparatively smaller portions of Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh, draining an area of 1.4 lakh Sq.km.
- It is bounded by the Central India hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and east, and by the Maikala range on the west.
- The Mahanadi (“Great River”) follows a total course of 560 miles (900 km).
- It has its source in the northern foothills of Dandakaranya in Raipur District of Chhattisgarh at an elevation of 442 m.
- The Mahanadi is one of the major rivers of the peninsular rivers, in water potential and flood producing capacity, it ranks second to the Godavari.
- Other small streams between the Mahanadi and the Rushikulya draining directly into the Chilka Lake also forms the part of the basin.
- The major part of the basin is covered with agricultural land accounting to 54.27% of the total area.
- It is one of the most-active silt-depositing streams in the Indian subcontinent.
- After receiving the Seonath River, it turns east and enters Odisha state.
- At Sambalpur, the Hirakud Dam (one of the largest dams in India) on the river has formed a man-made lake 35 miles (55 km) long.
- It enters the Odisha plains near Cuttack and enters the Bay of Bengal at False Point by several channels.
- Puri, at one of its mouths, is a famous pilgrimage site.
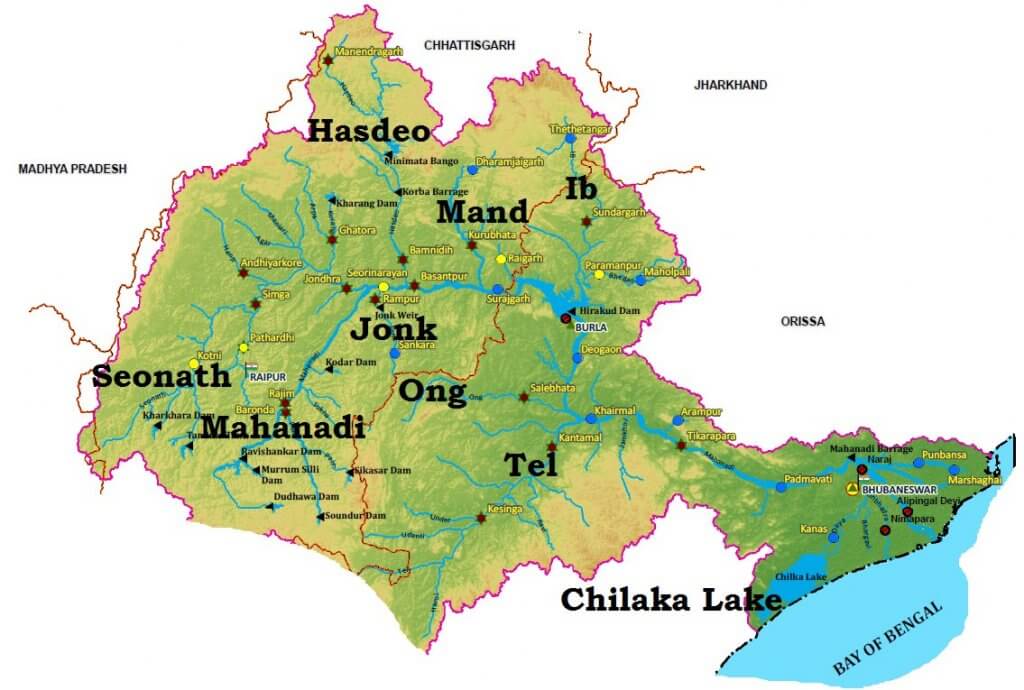
Tributaries of Mahanadi River
- Its upper course lies in the saucer-shaped basin called the ‘Chhattisgarh Plain’.
- This basin is surrounded by hills on the north, west, and south as a result of which a large number of tributaries join the main river from these sides.
- Left bank Tributaries: The Seonath, the Hasdeo, the Mand, and the Ib.
- Right bank Tributaries: The Ong, the Tel, and the Jonk.
SEONATH
- It originates from Panabaras Hill (625 m) and flows towards the north-east.
- The river feeds the inhabitants and industries of Durg District.
- The total length of the Sheonath River is 345km.
HASDEO
- The River originates from Chhattisgarh
- The total length of the river is 333km and the drainage areais9856sqkm
- The river flows towards the south of Chhattisgarh, through Bilaspur and Korba Districts
- Along the river lie rocks and hilly areas, thin forest areas.
MAND
- It is a left-bank tributary of Mahanadi
- Joins Mahanadi in Chandrapur before the river reaches Hirakud dam, the total length of the river is 241sqkm
- It drains an area in the range of 5200sqkm
- Mand River dam has been constructed in the Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh.
IB
- It is a left-bank tributary of Mahanadi River,
- Originates in hills in Raigarh district of Chhattisgarh
- The river runs for a distance of about 252km and drains an area of 12,447sqkm
- Ib river valley is famous for its rich coal belt.
ONG
- It is a right-bank tributary of the Mahanadi river.
- Flows across Orissa and joins Mahanadi at Sambalpur 11km up-stream of Sonepur where Tel merges.
- It drains an area of about 5128sqkm.
TEL
- Originating in the Nabarangpur district.
- Flows through the Kalahandi, balangir, and Sonpur districts of Orissa
- It is the second-largest river of Orissa.
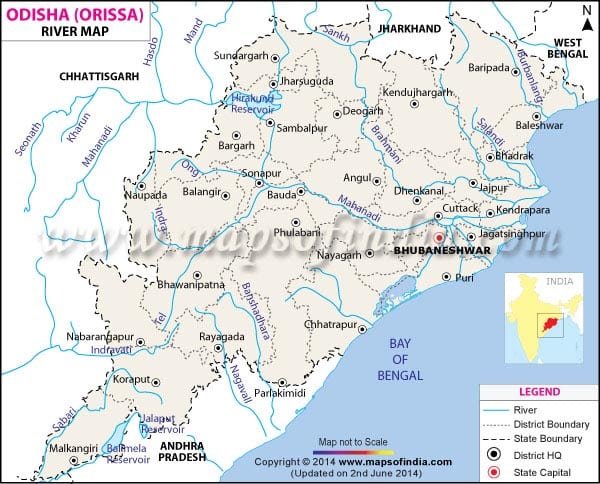
Kathajodi River
- Kathajodi River is an arm of the Mahanadi River in Odisha.
- It branches off at Naraj, then immediately is bifurcated. The southern branch, known as Kuakhai, which means Crow’s pool, and flows into the Puri district. Its mouth is closed by a bar, so that little water flows into it except at flood times.
- A little lower down from Cuttack the Kathajodi is bifurcated. The right branch is Sidhua and the left branch is Khatajodi.
- Cuttack City is situated between Mahanadi and Kathajodi.
- Other distributaries of Mahanadi include the Paika, Birupa, Chitroptala river, Genguti and Lun.
Sukapaika River
- Sukapaika is one of the several distributaries of the mighty Mahanadi river in Odisha.
- It branches away from the Mahanadi at Ayatpur village in Cuttack district and flows for about 40 kilometers (km) before rejoining its parent river at Tarapur in the same district.
- In the process, it drains a large landmass comprising over 425 villages.
- However, the river is undergoing sudden barrenness.
- It covers three blocks such as Cuttack Sadar, Raghunathpur and Nichintakoili of Cuttack.
- Sukapaika river is an important system of the Mahanadi to control floodwater and maintain the flow in the river as well as the Bay of Bengal.
Chitroptala River
- The Chitrotpala river is a river in Orissa state, India. It is a distributary of the Mahanadi, situated in both Kendrapara and Cuttack districts.
Important cities
Projects on Mahanadi River
- Two important projects completed during pre-plan period in the basin are the Mahanadi main canal and Tandula reservoir in Chhattisgarh.
- During the plan period, the Hirakud dam, Mahanadi delta project, Hasdeo Bango, Mahanadi Reservoir Project were completed.
The Hirakud Dam– It is one of the first major multipurpose river valley projects started after India’s independence. The dam aims at controlling floods in the Mahanadi basin, providing water for irrigation and municipal water supply. The dam is located near Sambalpur in the state of Odisha.
The Gangrel Dam– It is also known by the name of R.S. Sagar Dam. The dam is built across the Mahanadi river in Dhamtari district in the state of Chhattisgarh.
The Dhudhwa Dam– The dam is constructed across the Mahanadi river in Dhamtari district in the state of Chhattisgarh.
Industry in Mahanadi River Basin
- Three important urban centes in the basin are Raipur, Durg and Cuttack.
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favorable industrial climate.
- The Important industries presently existing in the basin are the Iron and Steel plant at Bhilai, aluminium factories at Hirakud and Korba, paper mill near Cuttack and cement factory at Sundargarh.
- Other industries based primarily on agricultural produce are sugar and textile mills.
- Mining of coal, iron and manganese are other industrial activities.
Floods in Mahanadi River Basin
- The basin is subject to severe flooding occasionally in the delta area due to the inadequate carrying capacity of the channels.
- The multi-purpose Hirakud dam provides some amount of flood relief by storing part of floodwater.
- However, the problem still persists and a lasting solution needs to be evolved.